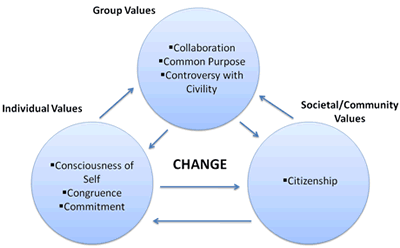
Leadership is the art of inspiring and guiding people to achieve common goals. The Social Change Model of Leadership (SCM) is a theoretical framework that emphasizes the importance of leadership in promoting social change. The SCM is based on seven dimensions, or values, called the “Seven C’s,” which work together to achieve the transcendent “C” of change. In this blog, we will discuss each of the seven values and their significance in promoting social change.
Consciousness of Self: The first value of the SCM is consciousness of self. It refers to the awareness of one’s own beliefs, values, and identity. It is essential for a leader to have a deep understanding of themselves before leading others. A leader who is conscious of themselves is more likely to act authentically and maintain their integrity while leading. Additionally, leaders who have a good understanding of themselves can connect with others and build relationships based on mutual respect and understanding.
Congruence: The second value of the SCM is congruence. It refers to the alignment between a leader’s actions and their values. A leader who acts in accordance with their values gains the trust and respect of others. Moreover, a leader who demonstrates congruence serves as a role model for others, inspiring them to align their own values and actions.
Commitment: The third value of the SCM is commitment. It refers to the dedication of a leader to a particular cause or group. Leaders who are committed to a common goal are more likely to persevere through challenges and setbacks. Additionally, leaders who demonstrate commitment inspire others to become dedicated and work hard towards achieving their goals.
Common Purpose: The fourth value of the SCM is common purpose. It refers to the shared goal or vision that unites a group. A leader who promotes a common purpose creates a sense of belonging and identity among members. Moreover, a leader who promotes a common purpose encourages members to work together and support one another towards achieving their shared goal.
Controversy with Civility: The fifth value of the SCM is controversy with civility. It refers to the ability of a leader to engage in productive and respectful dialogue, even in situations where there is disagreement or conflict. Leaders who are skilled at engaging in controversy with civility are more likely to reach consensus and make decisions that benefit the group as a whole.
Collaboration: The sixth value of the SCM is collaboration. It refers to the ability of a leader to work with others towards achieving a common goal. Leaders who promote collaboration create opportunities for members to contribute their unique skills and perspectives towards achieving the group’s shared goal. Moreover, leaders who promote collaboration build strong relationships among members, which fosters a sense of community and collective identity.
Citizenship: The seventh value of the SCM is citizenship. It refers to the responsibility of a leader to contribute to the well-being of their community. Leaders who demonstrate citizenship are committed to creating positive change in their community and promoting social justice. Moreover, leaders who promote citizenship inspire others to become active citizens and contribute to their community.
In conclusion, the Social Change Model of Leadership is a valuable framework that emphasizes the importance of leadership in promoting social change. The seven values of the SCM work together to achieve the transcendent “C” of change. Leaders who are conscious of themselves, demonstrate congruence, are committed to a common purpose, engage in controversy with civility, promote collaboration, and demonstrate citizenship are more likely to create positive change in their community.